Net Hire Ratio: What It Is, Why Use It, and How to Calculate It
Net Hire Ratio is a must-have recruiting metric in a data-driven HR culture. This guide will tell you everything you need to know about the Net Hire ratio and provide some best practice advice.
-
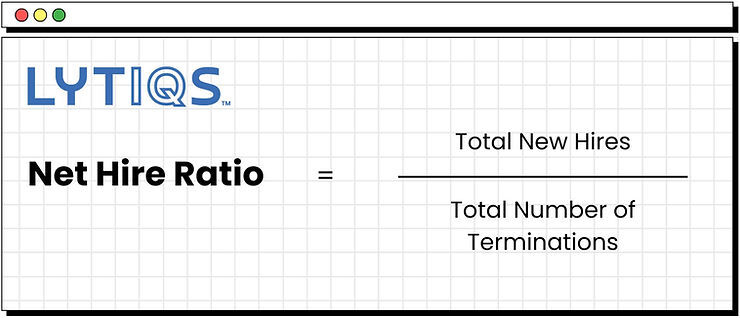
If the Net Hire Ratio is greater than 1, it means that the workforce has grown in size.
-
If the Net Hire Ratio is equal to 1, it means that the workforce size stays the same.
-
If the Net Hire Ratio is less than 1, it means the workforce shrank.
Many organizations do not have an easy way to proactively spot negative turnover trends among critical and core job roles. Usually, these trends only surface when an immediate intervention is required, or knowledge loss risk becomes an apparent issue.These job roles tend to be decentralized and scattered in various business lines and geographical locations. A few examples of recent job roles with unexpected talent shortages are cybersecurity roles, lab technicians, and accountants. Net Hire Ratio is a very effective metric that HR can use to take the first step in becoming more proactive in addressing their headcount and skill gaps.
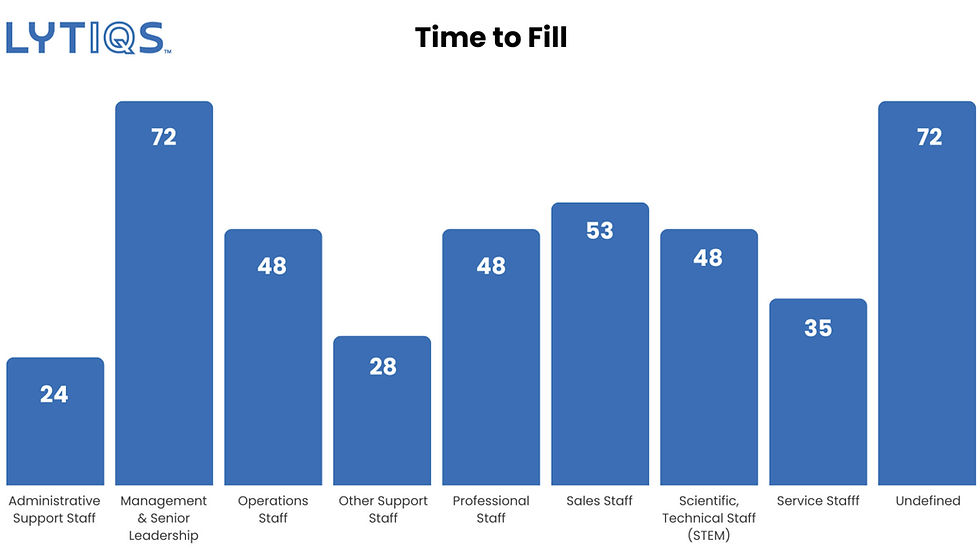
Where data allows, we recommend HR filter their Net Hire Ratio data by various workforce dimensions to gain valuable insight into the movement of talent across the organization. For example, HR can drill down the Net Hire Ratio to the job category level to see which part of the workforce is increasing or decreasing in size. For a hospital, this approach can be used to check if critical and hard-to-fill Nursing roles are growing, shrinking, or remaining flat. A well-thought-out job classification framework will be important to identify changes by workforce dimensions quickly and easily.
Because the Net Hire Ratio is a single metric that is very effective in capturing the changes in your workforce size, we recommend using this metric in combination with other workforce cost and productivity measurements such as Human Capital ROI Ratio and Total Cost of Workforce (TCOW) for workforce planning purposes. Recruiting teams can also use the Net Hire Ratio to set hiring targets and monitor results for different job categories, business lines, and geographical locations.